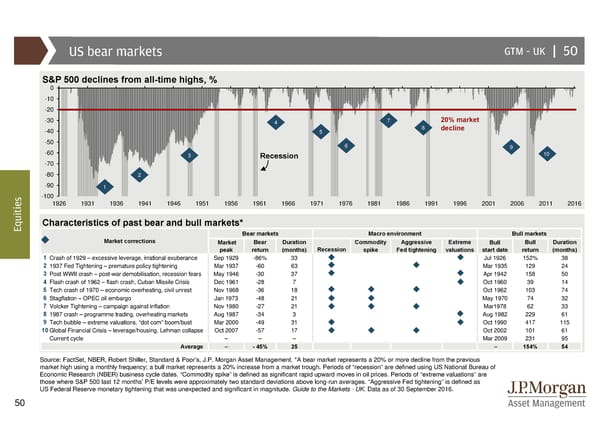
US bear markets GTM –UK | 50 S&P 500 declines from all-time highs, % 0 -10 -20 -30 4 7 20% market -40 5 8 decline -50 6 9 -60 3 Recession 10 -70 -80 2 -90 1 s -100 e 1926 1931 1936 1941 1946 1951 1956 1961 1966 1971 1976 1981 1986 1991 1996 2001 2006 2011 2016 i t i u Characteristics of past bear and bull markets* Eq Bear markets Macro environment Bull markets Market corrections Market Bear Duration Commodity Aggressive Extreme Bull Bull Duration peak return (months) Recession spike Fed tightening valuations start date return (months) 1 Crash of 1929 – excessive leverage, irrational exuberance Sep1929 -86% 33 Jul 1926 152% 38 2 1937 Fed Tightening – premature policy tightening Mar 1937 -60 63 Mar 1935 129 24 3 Post WWII crash – post-war demobilisation, recession fears May1946 -30 37 Apr 1942 158 50 4 Flash crash of 1962 – flash crash, Cuban Missile Crisis Dec1961 -28 7 Oct 1960 39 14 5 Tech crash of 1970 – economic overheating, civil unrest Nov 1968 -36 18 Oct 1962 103 74 6 Stagflation – OPEC oil embargo Jan 1973 -48 21 May 1970 74 32 7 Volcker Tightening – campaign against inflation Nov1980 -27 21 Mar1978 62 33 8 1987 crash – programme trading, overheating markets Aug1987 -34 3 Aug 1982 229 61 9 Tech bubble – extreme valuations, “dot com” boom/bust Mar 2000 -49 31 Oct 1990 417 115 10Global Financial Crisis – leverage/housing, Lehman collapse Oct 2007 -57 17 Oct 2002 101 61 Current cycle – – – Mar 2009 231 95 Average – - 45% 25 – 154% 54 Source: FactSet, NBER, Robert Shiller, Standard & Poor’s, J.P. Morgan Asset Management. *A bear market represents a 20% or more decline from the previous market high using a monthly frequency; a bull market represents a 20% increase from a market trough. Periods of “recession” are defined using US National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER) business cycle dates. “Commodity spike” is defined as significant rapid upward moves in oil prices. Periods of “extreme valuations” are those where S&P 500 last 12 months’ P/E levels were approximately two standard deviations above long-run averages. “Aggressive Fed tightening” is defined as US Federal Reserve monetary tightening that was unexpected and significant in magnitude. Guide to the Markets - UK. Data as of 30 September 2016. 50
 Guide to the Markets Page 49 Page 51
Guide to the Markets Page 49 Page 51